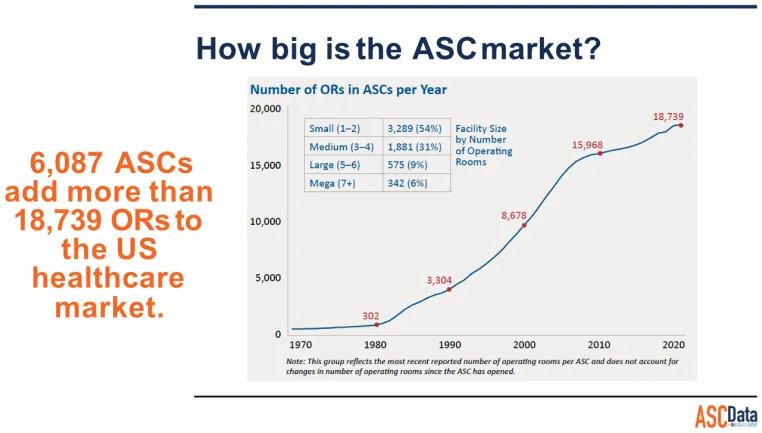
The number of surgical procedures performed outside of the traditional hospital setting has increased significantly. During the past two decades, freestanding outpatient surgery centers have represented one of the fastest growing health care settings. At the end of 1997, there were more than 2,600 such centers in the United States. In the same year, more than five million surgical procedures, led by ophthalmological and gastroenterological procedures, were performed in freestanding outpatient surgery centers. An additional 3.6 million minor surgical procedures were performed in physician office-based facilities. There are over eighteen thousand Ambulatory Surgery Centers in the US as of 2023.
Efficiency is the name of the game in ASCs so that providers can better maximize case volume and reduce costs. Equally as important as efficiency and cost is instrument cleaning and sterilization. Lack of standardization and a disorganized center is one where it’s easier for mistakes to happen. Standardized instructions and processes help reduce the risk of making costly errors and help to keep team members accountable. However, industry standards and regulations are in place for a reason: They help keep patients safe. Adopting best practices when it comes to the proper handling, cleaning and sterilization of instruments is critical to success.
Turning over surgical instruments in preparation for the next case helps keep costs down, aids time management and contributes to patient safety. However, if corners are cut to save time or mistakes made during instrument cleaning, preparation and sterilization, patients can develop surgical-site infections. Taking shortcuts is never a safe decision when it comes to cleaning patient care equipment and surgical instruments.
There are specific challenges that surgery centers must meet when sterilizing instruments specifically. First and foremost, ALL the sterilization devices MUST meet the correct regulations from the government, related to medical standards, otherwise you are subject to liability if a patient is infected. This is why defining proper sterilization guidelines in your ASC facility is so integral.
Developing and implementing an effective and practical sterilization process begins with knowing basic sterilization technology and existing recommended practice guidelines and standards for sterilization.
Each ASC must complete a CMS survey tool to build the annual risk assessment and program plan, otherwise knows as: AMBULATORY SURGICAL CENTER (ASC) INFECTION CONTROL SURVEYOR WORKSHEET. You must ask yourself, ‘Is your ASC compliant with AAMI AANSI guidelines for infection control & prevention? Can you confidently complete the CMS survey and show your ASC is compliant?’
The survey details specific procedures that must be adhered to, see below example:
III. Single Use Devices, Sterilization, and High Level Disinfection.
Pre-cleaning must always be performed prior to sterilization and high-level disinfection
Sterilization must be performed for critical equipment (i.e., instruments and equipment that enter normally sterile tissue or the vascular system, such as surgical instruments).
High-level disinfection must be performed for semi-critical equipment (i.e., items that come into contact with non-intact skin or mucous membranes such as reusable flexible endoscopes, laryngoscope blades).
Observations are to be made of staff performing equipment reprocessing (eg., surgical techs), unless these activities are performed under contract or arrangement off-site from the ASC.
Unless otherwise indicated, a "No" response to any question below must be cited as a deficient practice in relation to 42 CFR 416.51(a).
More information on the survey can be found here: https://www.cms.gov/medicare/provider-enrollment-and-certification/guidanceforlawsandregulations/ascs
What are common clinic issues that lead to incorrect sterilization?
Poorly designed healthcare facilities can lead to improper sterilization processes if the space was not designed to have ample room for necessary decontamination, instrument preparation and packaging and sterilization.
Lack of knowledge
At least one individual with infection prevention training should be hired by contract to help ensure instrument cleaning and sterilization processes meet national guidelines and standards of practice. This individual can manage the center’s infection prevention program and ensure all employees are thoroughly trained in the best sterilization practices.
Proper tracking
To improve health and reduce infections, ASCs must survey and track adherence to specific processes to reduce infection. Patients should also be educated about signs of infection and instructed to notify the facility if any symptoms of infection occur. When notified, all facilities must report the infection based on local, state, and federal requirements.
Regular surveillance and reporting emphasize the importance to all healthcare professionals of infection control protocols to reduce the likelihood of postoperative or post procedure infections.
Follow recommended precautions
All healthcare facilities should follow standard precautions, which are the minimum infection prevention practices that apply to all instances of patient care in any setting. These practices are in place to protect healthcare professionals and keep them from spreading infections among patients. Instrument cleaning and sterilization is the most important step in preventing the spread of infections, this includes the use of a washer-disinfector, an autoclave and the correct cleaning, testing and validation products.
Follow sterilization instructions on medical devices
All medical devices are labelled as reusable or single-use by the manufacturer. Improving sterilization processes in ambulatory settings requires healthcare professionals to stringently follow all sterilization and disinfection instructions to prevent transmitting infectious agents from patient to patient. Keep in mind that if the manufacturer does not provide cleaning and sterilization instructions, the device may not be intended for multi-patient use. Single-use medical devices should never be reused. Even if the manufacturer provides detailed cleaning and sterilization instructions, if your setting doesn’t have the resources to follow the instructions as written, then that device should not be reprocessed.
It is important to understand that outdated sterilization equipment is very unreliable. Though older equipment may be familiar and feel safe, older sterilization technology is much more prone to malfunctions and becomes less effective over time, making it unreliable. Additionally, not having enough equipment to meet demand is an equally significant problem, resulting in postponed procedures and unhappy patients. Which is why the ASC should have the correct size and number of sterilization devices to meet the demands of the clinic needs.
While investing in new equipment comes with a high initial cost, it saves healthcare facilities much more than money in the long run. Newer sterilization technology is more dependable and won’t cost hospitals and ASCs as much in lost time due to maintenance outages. Many modern sterilization solutions are energy efficient, meaning less power consumption and lower energy bills.
Sterilization devices have advanced over the past few years, with wi-fi and connectivity capabilities, with features of advanced tracking and documentation by sophisticated software. A critical part of the sterilization process is the identification and traceability of packages and documentation of the process, including results of the process monitoring. In the event of a sterilization failure, good record keeping will facilitate quick and efficient tracking of all packs within that particular load. Newer autoclaves can provide printers and proper documentation software.
Using autoclaves that do not meet regulatory standards is so critical to your ASC’s success. Falling short of these standards carries serious consequences for healthcare facilities and can lead to loss of accreditation or hefty penalties and fines.
Cleaning and maintenance
All Instrument and autoclave device manufacturers should provide specific cleaning and decontamination procedures. Cleaning procedures may depend on the complexity of the instrument to be cleaned. Some devices must be partially disassembled to achieve proper cleaning. In physician office settings, most of the cleaning is done by hand or in ultrasonic cleaning units. Larger surgery centers may have disinfectors or washer units that can effectively clean and wash many types of instruments.
After instruments and devices have been thoroughly cleaned and decontaminated, they must be inspected for cleanliness and tested for functionality. All surfaces should be visually inspected to verify cleanliness. Functionality testing involves verification of device performance (eg, sharp edges, smooth operation of moving parts). Complex instruments should always be inspected and tested for functionality according to manufacturer instructions.
In Conclusion, at the end of the day sterilization monitoring is the only practical method to provide assurance that all the critical parameters of sterilization have been met. A wide variety of sterilization monitoring can be performed to provide sterility assurance. Establishing the best possible sterilization program begins with education and knowledge of recommended practices and standards relating to sterilization. Policies and procedures for every step of the sterilization process then can be developed. ASCs must prioritize patient safety and adhere to stringent guidelines and regulations to maintain a sterile environment.
Tuttnauer medical devices meet all ASC regulatory standards, ensuring safety and product high quality reliability.
